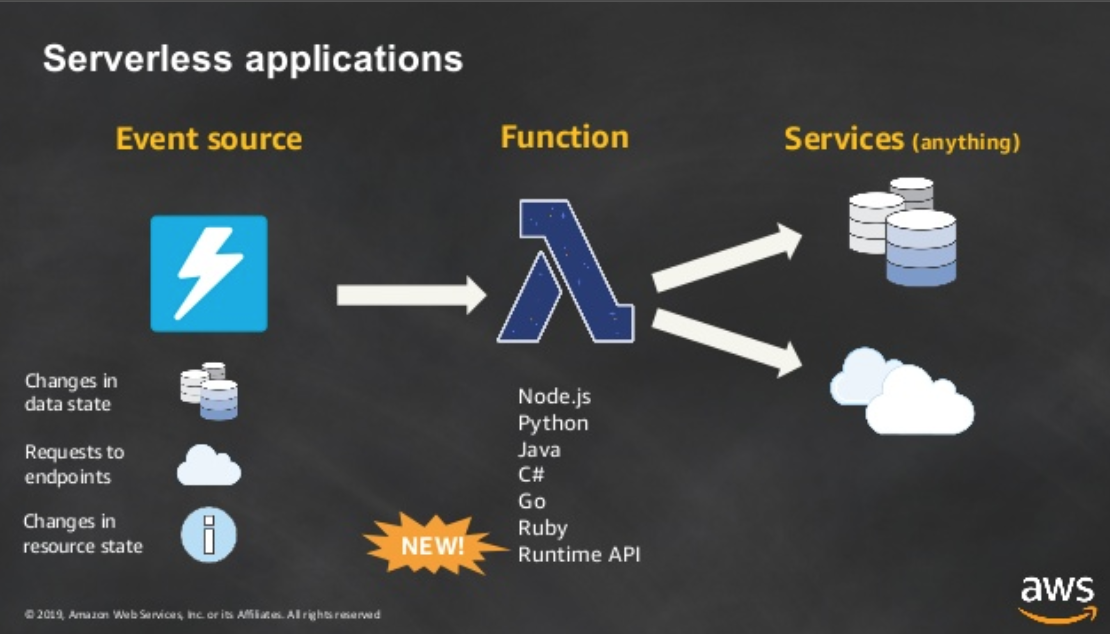
Try to use Serverless function
Platform that I’ll try
AWS
https://www.slideshare.net/AmazonWebServices/deep-dive-into-aws-sam
GCP
-
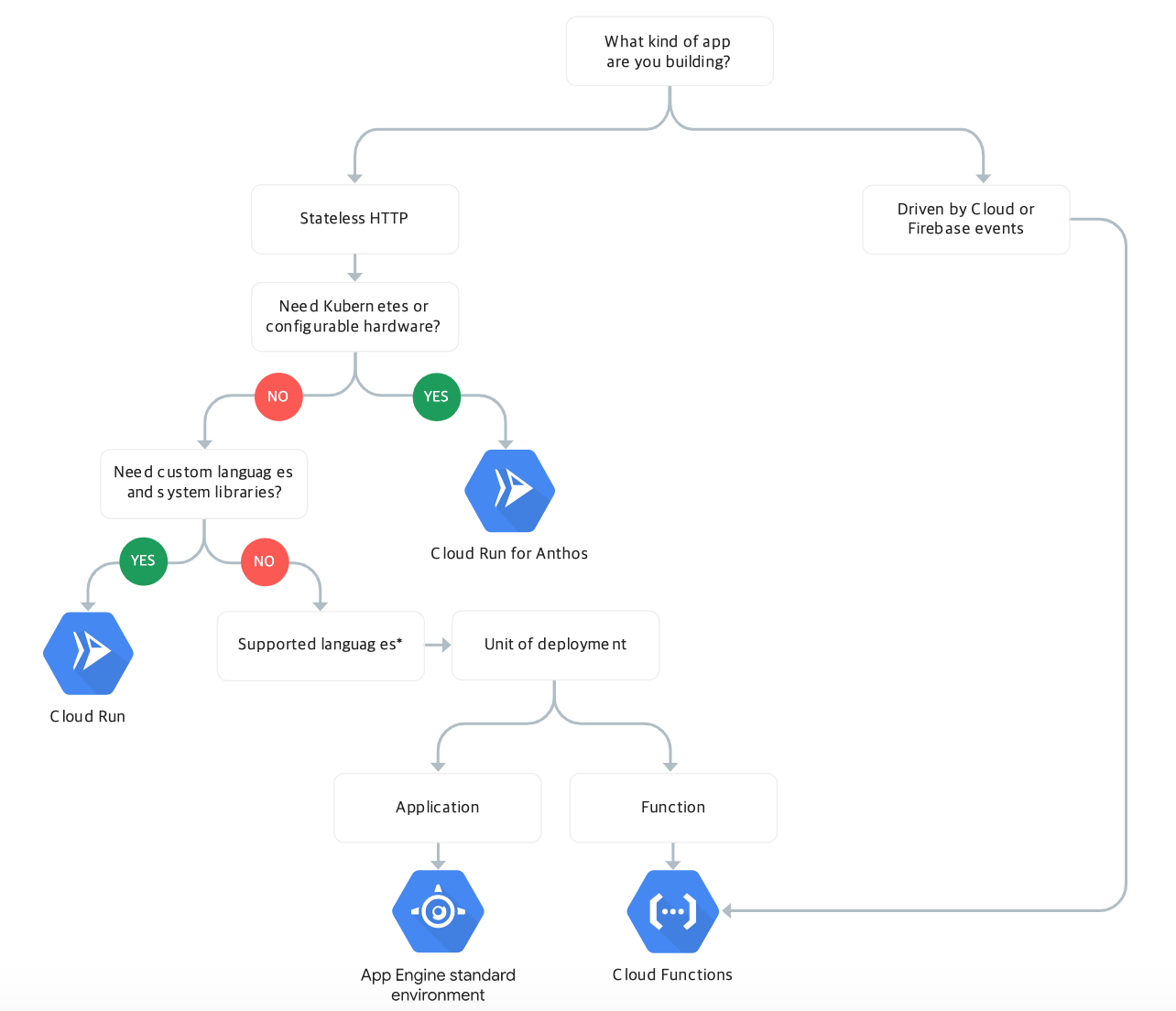
Very similar to AWS. Basic concepts are do something when the event happens and there are several choices below. In this article, I’ll research the Cloud Functions only.
Writing code in Python
AWS SAM (Serverless Application Model)
Building the environment
There are so many tutorials to build the serverless function on AWS in Youtube so I’ll not mention it.
Use SAM(Serverless Application Model) to develop. Just check the document to install on various OS environments.
If you got the output like following, then you succeed to install SAM.
% sam --version
SAM CLI, version 0.40.0
- Build the project with the basic template: `sam init`
- If you create the python project, then check your python version and choose your python version exactly.
% sam init
Which template source would you like to use?
1 - AWS Quick Start Templates
2 - Custom Template Location
Choice: 1
Which runtime would you like to use?
1 - nodejs12.x
2 - python3.8
3 - ruby2.5
4 - go1.x
5 - java11
6 - dotnetcore2.1
7 - nodejs10.x
8 - python3.7
9 - python3.6
10 - python2.7
11 - java8
12 - dotnetcore2.0
13 - dotnetcore1.0
Runtime: 8 <== If you choose the wrong python version, then it will make the build error.
Project name [sam-app]: my-sam-py
Cloning app templates from https://github.com/awslabs/aws-sam-cli-app-templates.git
AWS quick start application templates:
1 - Hello World Example
2 - EventBridge Hello World
3 - EventBridge App from scratch (100+ Event Schemas)
Template selection: 1
-----------------------
Generating application:
-----------------------
Name: my-sam-py
Runtime: python3.8
Dependency Manager: pip
Application Template: hello-world
Output Directory: .
Next steps can be found in the README file at ./my-sam-py/README.md
Now move my-sam-py and open that folder by VS.code IDE.
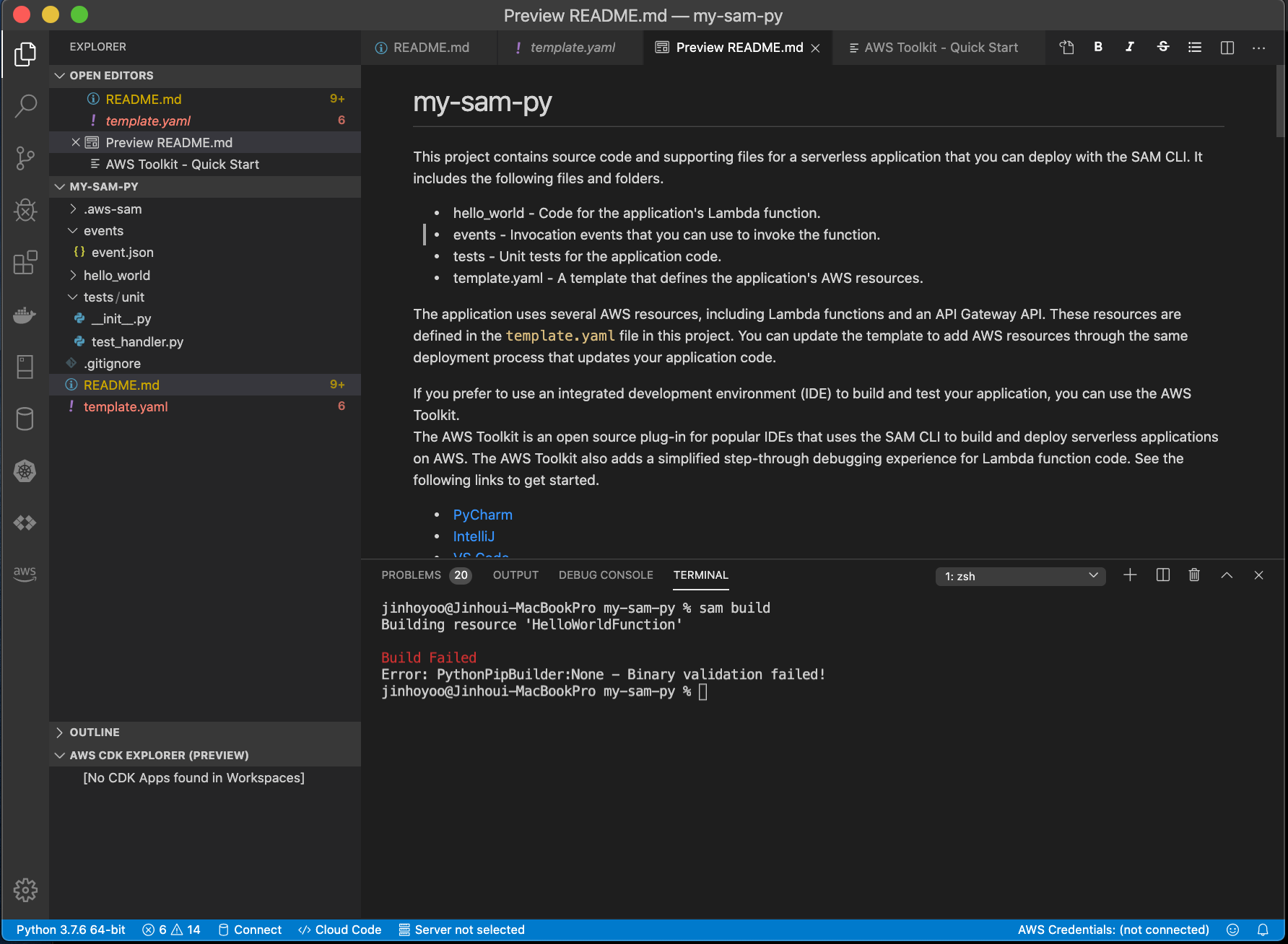
To build that project, use sam build. This process is integrating the dependencies to execute this function. Lastly, it will create the docker image and deploy it on AWS.
Running the API on the local machine
Use sam local. You can launch and request this API on the local machine.
sam local start-api: Launch API on the local machine.- Request the laucnhed API server : Call API by
curl. If you call this API you created, then usecurl [http://127.0.0.1:3000/hello](http://127.0.0.1:3000/hello).
You can get the following result if you call the API by curl.
% sam local start-api
Mounting HelloWorldFunction at http://127.0.0.1:3000/hello [GET]
You can now browse to the above endpoints to invoke your functions. You do not need to restart/reload SAM CLI while working on your functions, changes will be reflected in
stantly/automatically. You only need to restart SAM CLI if you update your AWS SAM template
2020-01-11 22:56:46 * Running on http://127.0.0.1:3000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
Invoking app.lambda_handler (python3.7)
Fetching lambci/lambda:python3.7 Docker container image......
Mounting /Users/jinhoyoo/Documents/serverless/my-sam-app/.aws-sam/build/HelloWorldFunction as /var/task:ro,delegated inside runtime container
START RequestId: d1e1793c-81be-19a7-b45c-a27a3e492bda Version: $LATEST
END RequestId: d1e1793c-81be-19a7-b45c-a27a3e492bda
REPORT RequestId: d1e1793c-81be-19a7-b45c-a27a3e492bda Init Duration: 185.19 ms Duration: 4.94 ms Billed Duration: 100 ms Memory Size: 128 MB Max Memory
Used: 23 MB
No Content-Type given. Defaulting to 'application/json'.
2020-01-11 22:57:03 127.0.0.1 - - [11/Jan/2020 22:57:03] "GET /hello HTTP/1.1" 200 -
You can feel that it seems slower than requesting the API to implement the webserver from scratch. It downloads the docker image including AWS lambda runtime. The most important log is the following.
REPORT RequestId: d1e1793c-81be-19a7-b45c-a27a3e492bda Init Duration: 185.19 ms Duration: 4.94 ms Billed Duration: 100 ms Memory Size: 128 MB Max Memory
Used: 23 MB
Especially, it prints ‘Max Memory Used’ that consume the memory size to execute this function, CloudWatch will monitor this value. ( Then 23MB is real value?)
You can test this API without using the curl.
% sam local invoke "HelloWorldFunction" -e events/event.json
Invoking app.lambda_handler (python3.7)
Fetching lambci/lambda:python3.7 Docker container image......
Mounting /Users/jinhoyoo/Documents/serverless/my-sam-app/.aws-sam/build/HelloWorldFunction as /var/task:ro,delegated inside runtime container
START RequestId: 2724f27e-a31f-1eda-00c8-7b33becc1270 Version: $LATEST
END RequestId: 2724f27e-a31f-1eda-00c8-7b33becc1270
REPORT RequestId: 2724f27e-a31f-1eda-00c8-7b33becc1270 Init Duration: 163.04 ms Duration: 4.51 ms Billed Duration: 100 ms Memory Size: 128 MB Max Memory
Used: 23 MB
{"statusCode":200,"body":"{\"message\": \"hello world\"}"}
This operation calls the API with events/event.json that has the data on how to call this API. You can generate event file by using sam local generate-event.
Addtionally, read this document to know the command for build.
# Build a deployment package
sam build
# Run the build process inside an AWS Lambda-like Docker container
sam build --use-container
# Build and run your functions locally
sam build && sam local invoke
# Build and package for deployment
sam build && sam package --s3-bucket <bucketname>
# For more options
sam build --help
Debug on VS.code
In general case, we can put the breaking point on the code and run the debugger in real-time on the IDE. But you should use remote debugging to debug the API built by SAM toolbox. Read this document for the detail.
Deploy
$ sam build --use-container
$ sam deploy --guided
GCP - Cloud Function
Building the environment
Contrary to using SAM, GCP can make API function by creating a python code. First of all, install the GCP CLI Tool. Please read this document to understand the overview.
Create themain.py that uses flask module and the requirments.txt to get the dependency of flask.
main.py
from flask import escape
def hello_http(request):
"""HTTP Cloud Function.
Args:
request (flask.Request): The request object.
<http://flask.pocoo.org/docs/1.0/api/#flask.Request>
Returns:
The response text, or any set of values that can be turned into a
Response object using `make_response`
<http://flask.pocoo.org/docs/1.0/api/#flask.Flask.make_response>.
"""
request_json = request.get_json(silent=True)
request_args = request.args
if request_json and 'name' in request_json:
name = request_json['name']
elif request_args and 'name' in request_args:
name = request_args['name']
else:
name = 'World'
return 'Hello {}!'.format(escape(name))
requirements.txt
Flask==1.0.2
Running the API on the local machine
I suppose nothing to do on the local machine. As you see, it implements the function that gets the request object of the flask framework as a function argument. If you run this function on the local machine, you have to implement your own main function but this main function is implemented in cloud function service so hard to do on the local machine.
Debug on VS.code
As I mentioned before, nothing to do.
Deploy
You can deploy the function like following.
$ gcloud functions deploy hello_http --runtime python37 --trigger-http
Then you can get the output.
$ gcloud functions deploy hello_http --runtime
python37 --trigger-http
Allow unauthenticated invocations of new function [hello_http]? (y/N)?
y
Deploying function (may take a while - up to 2 minutes)...WARNING: Setting IAM policy failed, try "gcloud alpha
functions add-iam-policy-binding hello_http --member=allUsers --role=roles/cloudfunctions.invoker"
Deploying function (may take a while - up to 2 minutes)...done.
availableMemoryMb: 256
entryPoint: hello_http
httpsTrigger:
url: https://us-central1-jinho-experimental.cloudfunctions.net/hello_http
labels:
deployment-tool: cli-gcloud
name: ~~~~
runtime: python37
serviceAccountEmail: jinho-experimental@appspot.gserviceaccount.com
sourceUploadUrl: https://storage.googleapis.com/gcf-upload-us-central1-51e50952-d19b-4fb9-8af1-bad5bcb4fca9/b5a9
~~~~~~~~
status: ACTIVE
timeout: 60s
updateTime: '2020-01-13T05:47:32Z'
versionId: '1'
You can get the URL on the httpsTrigger field. You can get this URL by using the command below.
$ gcloud functions describe hello_http
availableMemoryMb: 256
entryPoint: hello_http
httpsTrigger:
url: https://us-central1-jinho-experimental.cloudfunctions.net/hello_http
labels:
deployment-tool: cli-gcloud
.....
You can request this API by curl like the following.
$ curl "https://us-central1-jinho-experimental.cloudfunctions.net/hello_http?name=BOB"
Hello BOB!%
I confirmed it works on GCP console too.
Conclusion
I suppose AWS SAM itself is the masterpiece that integrates all serverless features. But the complexity of AWS, CloudFormation is the root cause, is too big so I’m not confident to operate the service well.
GCP uses the many industry-standard techs so it doesn’t seem too complex. The problem is hard to debug or test on the local machine. And I cannot find any tool for this.
Overall, it seems still difficult to implement some features by using serverless only. I suppose it fits the trigger for some event.
References
- AWS SAM tool tutorial
- Deep dive into AWS SAM and AWS SAM CLI
- Google cloud functions tutorial
- Serverless with Google cloud functions
- Serverless with Google cloud
One More Thing
Have you ever heard about ainized project? It seems the future of serverless service. Have fun! ;-)